Neutron Lifetime measurement
The particles that make up a substance decay into smaller particles at a certain rate per unit time. And the time at which the number of particles decreases to 1/e is called the lifetime.
And also, free neutrons βdecay into protons, electrons, and antielectron neutrinos in about 15 minutes.
Neutron lifetime is an important parameter in elementary physics.
(1)Big Bang Nucleosynthesis Theory
It is said that the same number of protons and neutrons were produced at the moment of the Big Bang, which is said to be an explosion at the beginning of the universe.
Neutron lifetime is about 15 minutes compared to protons, which hardly decays. As time passes, the balance between protons and neutrons is lost, and nuclei are synthesized with a certain probability.
The theory predicts quantity of formed nucleus in the early universe from the probability of proton/neutron coupling predicted from density of matter.
This theory is called the Big Bang nucleosynthesis theory.
Since the number of neutrons after the Big Bang is determined by the lifetime, the neutron lifetime is an important parameter of the Big Bang nucleosynthesis theory.
(2)Unitarity verification of CKM matrix
The element Vud of the CKM (Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Masukawa) matrix representing the properties of quarks in the standard model can be obtained from the neutron lifetime.
Vud is an important parameter for the unitarity verification of CKM matrix, so it is possible to verify the standard model from the experimental results.
There are two main methods for neutron lifetime measurement.
(a)In-Beam method
This is a method to determine the neutron lifetime from the ratio of incident neutron flux to the number of β decays in the time of passing through a region of beam-like neutrons.
(b)Storage method
Neutron energies below 25 neV (ultracold neutron) are below the Fermi potential, such as nickel.
Therefore, a bottle with a neutron reflector on its inner wall can accumulate neutrons.
This is a method to determine the neutron lifetime from the number of neutrons remaining in the bottle after accumulating neutrons for certain time.
However, there is a difference of 8 seconds between the neutron lifetime values measured by these two methods.
The 8 second discrepancy is called the Neutron Lifetime Puzzle, and it remains to be seen whether it is due to systematic errors from each methods or unknown physics.
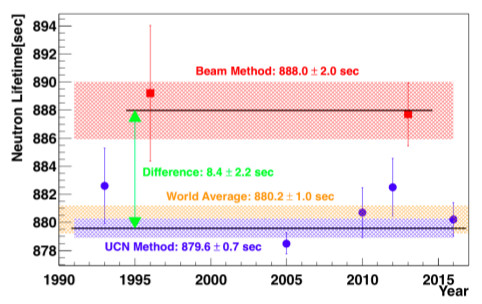
Therefore, at MLF BL05 of J-PARC, we are conducting neutron lifetime measurement experiments using TPC (Time Projection Chamber) which has different systematic errors from these two methods.
And, we aim to decide neutron lifetime with an accuracy of 1 second (0.1%).
Using a spin flip chopper, we make a neutron bunch (a mass of neutrons) that fits in the TPC.
The neutron lifetime is determined by simultaneously detecting "Neutron βdecay" and "Reaction of Neutron with TPC Operating Gas 3He (lead to the incident neutron flux)" in the TPC.
We are currently deriving the neutron lifetime with an accuracy of 20 seconds (2%).
Therefore, we aim to achieve higher accuracy by updating the upstream optical system to improve the statistical accuracy and analyzing to improve the systematic error.

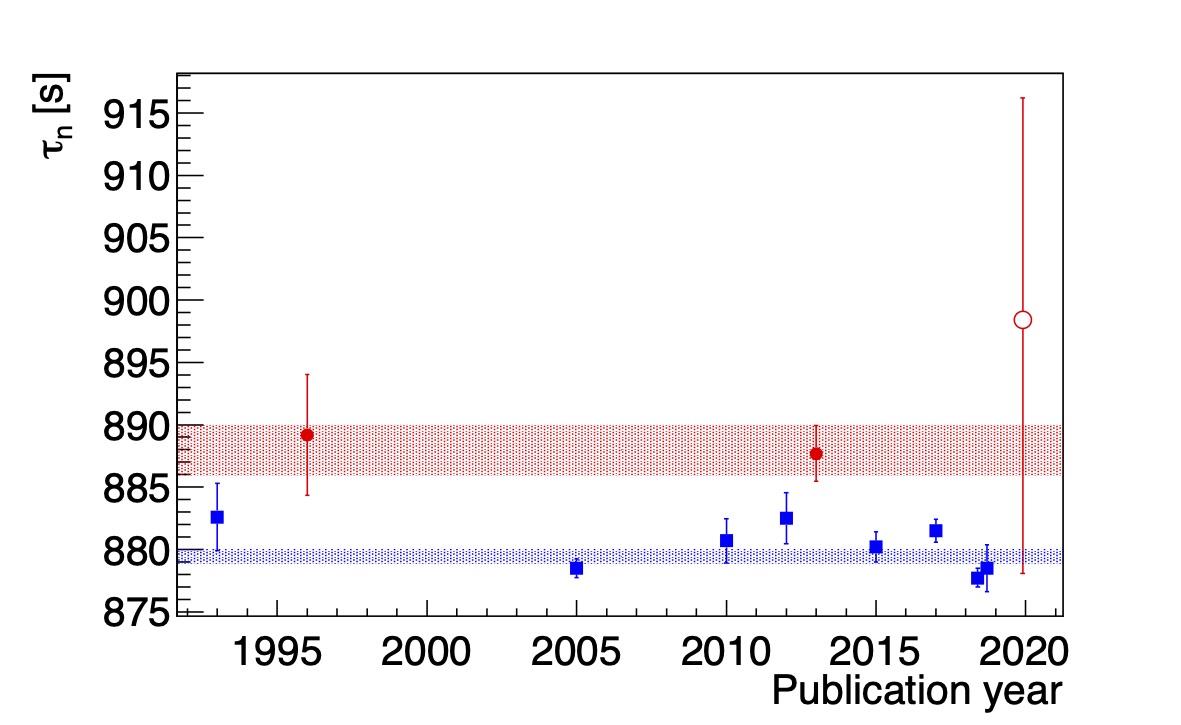
(left)J-PARC MLF BL05 (right)Our result (arXiv:2007.11293 (2020))



